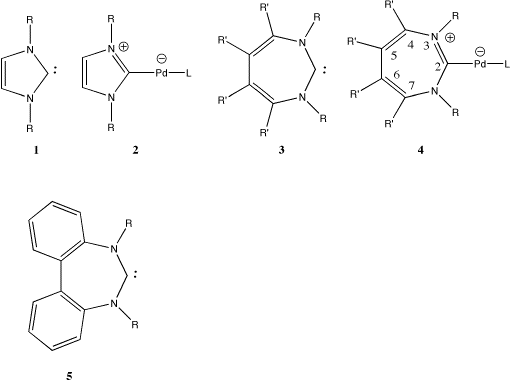
| Table 1. Computed B3LYP/DZVP Energies, Geometries and NICS values for 1-4.§ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure; Substituents | Energy, Hartree (B3LYP/dzvp) | NICS, ppm | Geometrya | Point Group Symmetry (Ring) | DE Coordination (Kcal/mol)b | |
| 2; R=CH3, L=P(Me)3 | -5705.7038 | -10.8 | 2.13,1.37,1.39,1.36; 0.0 | C2v | -9.4 | |
| 1; R=CH3 | -304.8242 | -11.8 | 1.37,1.39,1.36; 0.0 | C2v | - | |
| 4; Z=C, R,R',R"=H, L=P(Me)3 | -5704.4513 | 14.7 | 2.10,1.37,1.43,1.34,1.47; 22.43 | C2 | -8.4 | |
| 4; Z=C, R,R',R"=H, L=PH3 | -5586.4758 | 15.0 | 2.12,1.36,1.43,1.34,1.47; 22.69 | C2 | -12.5 | |
| 4; Z=C, R,R',R"=H, L=PH3 | 0.5c | 22.7 | 2.12,1.36,1.43,1.34,1.47; 0.0 | C2v | - | |
| 3; Z=C,R,R',R"=H | -303.5733 | 19.2 | 1.36,1.43,1.34,1.47; 18.45 | C2 | - | |
| 4; Z=C, R=H,R',R"=F, L=PH3 | -5983.4949 | -1.4 | 2.08,1.37,1.41,1.34,1.45; 34.06 | C2 | -10.8 | |
| 4; Z=C, R=H, R',R"=F, L=PH3 | 7.1c | 12.2 | 2.10,1.36,1.42,1.34,1.47; 0.0 | C2v | - | |
| 3; Z=C, R=H, R',R"=F | -700.5951 | 0.3 | 1.37,1.41,1.34,1.45; 34.68 | C2 | - | |
| 4; Z=C, R,R',R"=CH3, L=PH3 | -5822.3607d | 3.9 | 2.15,1.37,1.45,1.35,1.48; 46.16 | C2 | -12.3 | |
| 3; Z=C, R,R',R"=CH3 | -539.4585 | 5.6 | 1.37,1.45,1.35,1.48; 47.59 | C2 | - | |
| 4; R=CH3,R'+R"=benzo, L=PH3 | -5972.4158 | 5.3 | 2.14,1.37,1.44,1.41,1.48; 43.31 | C2 | -10.7 | |
| 4; R=CH3,R'+R"=benzo, L=PH3 | 21.7c | running | 2.28,1.36,1.45,1.43,1.51; 0.0 | C2v | - | |
| 3; R=CH3,R'+R"=benzo | -689.5161 | 6.9 | 1.37,1.44,1.41,1.48; 45.36 | C2 | - | |
| 4; Z=Si, R,R',R"=H, L=PH3 | -5837.9274 | 9.9 | 2.30,1.74,1.42,1.35,1.47; 25.70 | C2 | -12.0 | |
| 4; Z=Si,R,R',R"=H, L=PH3 | 0.5c | 14.8 | 2.30,1.73,1.42,1.35,1.47; 0.0 | C2v | - | |
| 3; Z=Si,R,R',R"=H | -555.0256 | 12.5 | 1.75,1.42,1.35,1.47; 25.15 | C2 | - | |
| 4; Z=Si, R=H, R',R"=F, L=PH3 | -6234.9566 | -2.2 | 2.27,1.75,1.39,1.34,1.45; 40.79 | C2 | -11.7 | |
| 4; Z=Si, R=H,R',R"=F, L=PH3 | 7.9c | 8.1 | 2.27,1.74,1.40,1.34,1.40; 0.0 | C2v | - | |
| 4; Z=Si, R=H,R',R"=F | -952.0553 | -0.8 | 1.77,1.39,1.34,1.45; 41.40 | C2 | - | |