Chemistry and climate change
Find out our position on climate change
For nearly three decades the United Nations have been bringing together almost every country on earth for global climate summits, with the first conference held in Berlin in 1995. At these annual meetings, governments discuss how to mitigate and prepare for climate change.
We look forward to the next conference, COP29, coming up in November 2024. We have been gathering perspectives from around the chemical science community illustrating how chemistry is vital to understanding and tackling climate change.
On this page
Solar chemicals
Solar photovoltaic panels are delivering low-cost power around the world and form a major part of global efforts to tackle climate change. Less well known are the reactions and devices that could support a similar transformation of industrial chemical systems and fertiliser production. Nature does this all the time as through photosynthesis and subsequent reactions which create complex molecules to store energy and grow leaves, trunks and roots.
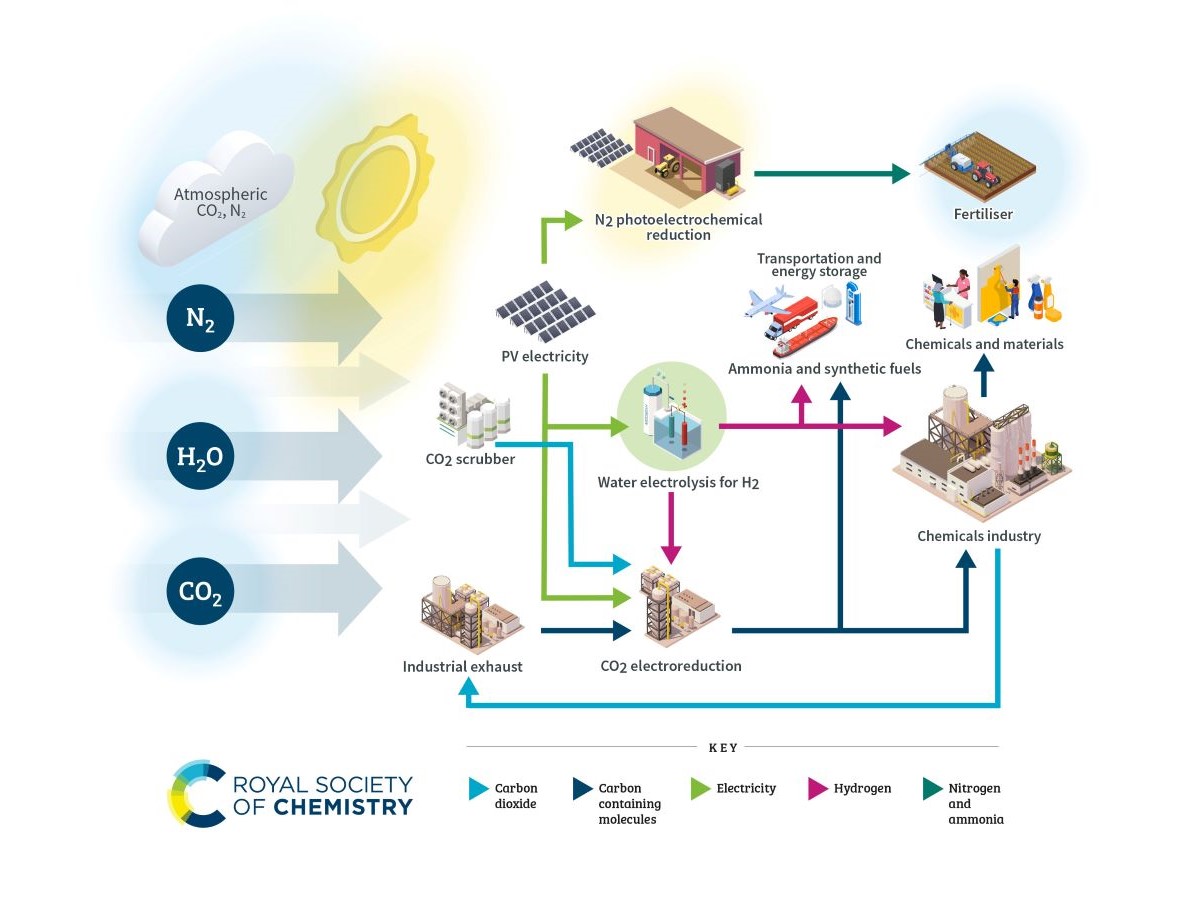
A range of different approaches are being investigated to harness this potential. Water, nitrogen and carbon dioxide from the environment can be combined in different ways using electrical energy from solar PV cells. Other pathways use photocatalytic materials that absorb light to facilitate reactions. These photocatalysts can be inorganic, transition metal compounds or biological molecules like enzyme complexes and chlorophyll centres. Biohybrid devices go further and incorporate parts of living organisms or whole genetically modified organisms in artificial surroundings to direct reactions towards desirable chemical compounds.
Solar chemical systems can already produce hydrogen and simple carbon containing molecules in the laboratory. However, they could ultimately be used to make many different consumer products such as plastics and paints, or fuels for aircraft and ships. Processes might take different forms; at an industrial scale, for instance using the waste carbon dioxide from chemical plants or power stations, or combined in small scale reactors, such as devices to produce fertiliser directly on farms.
To find out more about solar chemicals, their development and future applications visit the Solar Chemicals network and watch our webinar with leading experts in the field.
Understanding and tackling climate change: previous events
In recent years, we have convened a series of events on chemical science’s role in tackling sustainability and climate change challenges, exploring opportunities and inspirational stories from across our global chemical science community, including many speakers from the Faraday Institution, the UK's flagship battery research programme. You can watch the recordings below.
Batteries and energy storage
This panel discussed the cutting edge chemistry underlying next generation battery innovations, their potential, their limitations and their pathways to mass adoption.
Beyond lithium ion batteries
Solar fuels and chemicals store energy from sunlight in chemical bonds using abundant resources such as water and carbon dioxide. The products can be used directly as fuels or the building blocks of other useful chemicals.
Solar fuels and chemicals
This panel discussed the latest research to develop pathways for the recycling and recovery of critical raw materials in batteries, to reach a circular economy.
The circular economy of batteries
An engaging and accessible panel discussion, summarising the amazing science showcased at the recent Chemical Science Symposium.
Approaches for sustainable energy conversion
This panel discussed the latest chemistry which may open up a new hydrogen economy as we replace fossil fuels in power, transport and industry.
Hydrogen production and use
This panel discussed the opportunities and limitations of batteries in the context of global development and where science and innovation can improve them towards achieving the United Nations SDGs.
The chemistry of hydrogen production and use
Chemistry and climate change
The air quality problem and the chemistry behind it. Innovations in remote sensing and the use of drones, the chemistry of combustion, and the technologies that can be deployed.
Air quality and climate protection
Metal Organic Frameworks are a hot topic and many potential uses including hydrogen storage, water and carbon capture, and cleaning up air pollution.
MOFs for energy and environment
Discussing the potential for Nature Based Solutions (NBS) to tackle climate change and the carbon flows and storage in different ecosystems.
The chemistry of nature based solutions
This panel event summarised progress on using waste CO2 to make some of the most important materials for modern society: polymers, plastic, fuels, and cement.
Carbon dioxide utilisation
This panel discussed the intersecting issues of plastic and climate change, alternative raw materials, and the impact of dealing with plastic waste.
Plastics and climate change
This panel discussed how wildfires affect soil, air, and water. Watch the video to see how the chemical sciences can deliver a big impact in addressing this global challenge.
Wildfires: influence on air, soil, and water
This panel discussed how materials chemistry underpins many technologies and industries and how advances can increase sustainability.
Materials chemistry enabling sustainability
This panel summarised our understanding of CO2 and methane, their agricultural sources, what can be done and where further research is focussed.
Climate impacts of agriculture
Experts from academia and industry discuss the steps organisations and individuals working in science can take to reduce emissions and identify the challenges that remain.
The net zero laboratory
Education and careers
Please see our Education in Chemistry website to view a series of sustainability-themed resources for secondary teachers and students.
Our website A Future in Chemistry illustrates the breadth of opportunities for chemists and students who want a career tackling climate change. Find out more about developing coatings for wind turbines, new ways of recycling batteries, making leather substitutes from pineapple waste and lots more.
COP26 #PoweredByChemistry
Across the COP series, we have been focusing on chemistry’s unique opportunity to bridge the gap between the SDGs; in particular Goal 12 (responsible consumption and production) and Goal 13 (climate action).
COP26 #PoweredByChemistry
Our SME showcase
Our small and medium enterprise community (SME) is offering innovative solutions to the big sustainability challenges of the day. The videos below show SMEs representing different solutions ranging from solar energy to fast charging battery technologies.
Carbon capture and utilisation offers a solution to turning the abundance of waste CO2 from industry into something useful. Chemistry SME ViridiCO2 tells us about their new catalytic technology, which transforms CO2 into polymers for use in everyday products, while at the same time using CO2 instead of fossil fuels to carry out their processes. Watch their story:
Carbon capture
Solar power is a clean and sustainable power source, but innovation is needed to make it more efficient, useful and cost less. Oxford PV have developed a tandem solar cell, using perovskite and silicon, that has resulted in record breaking efficiency. Watch their video to find out how:
Solar power
SME Echion Technologies have developed a safe, fast charging battery technology based on sustainable materials which can be charged much faster than current batteries and for many more cycles. This will accelerate the electrification of trains, buses and other vehicles, helping overcome the challenge in the race to zero emissions transport. Watch their story:
Fast charging batteries
Green hydrogen is CO2 free at the point of generation. It has applications in heating homes, industrial fuels, and powering transport options from cars to planes. In this SME showcase, TFP Hydrogen Products Ltd tell us about how their products will contribute to net zero goals.